I’ve been using this method of bringing my cables in for a few years now:
Car Portable Cable Access
And whilst this has been OK it has some drawbacks. Once while packing away it blew away so I am actually using the 2nd incarnation! It forces the cables to the very top of the window by design which for stiffer coax like the LBC400 I use can make it awkward to pass it to the far side of the car for the weekend contests using amp(s). Also bugs manage to locate the very small gap there is and attack me as the light it directly above my head in the car.
So time for a new one. Clive G8LNR showed me pics of his which is a piece of thin ply and a letterbox. The letterbox I thought was a great idea so I decided to steal that idea.
So here I describe the making of my improved car portable cable access.
I wanted to make mine inherently waterproof so plastic was the obvious choice so I asked my friend Paul who ran a plastic injection molding company the best plastic to use and he recommended polypropylene so I got some 3mm sheet after measuring the window which was 4mm thick. Some places did 3mm and 5mm, some did 3mm and 4.5mm and some did 3mm and 4mm, alegedly. Following my Moulder principal of trust no-one, I ordered 3mm as I wanted to ensure it would fit into the same channels in the door as the glass does.
Checking the dimensions of letterboxes I realised that I needed the maximum opening I could get at the door pillar end of the glass. I started off by scribing the window curve onto cardboard, cutting the sides to shape then opening the window to the desired amount and scribing the curve again. I had to make a second cardboard one as the ends were truncated but soon had that test fitted:

Then a case of taping that to my 1000 x 500mm sheet of polypropylene to trace ready for cutting:

I then cut this out with a jigsaw using a metal cutting blade. After deburring it was time for the moment of truth. To fit it I would have the window down and insert the narrow end by the door pillar then flex it so I could insert it into the opposite channel then slide it up into the top channel. Then carefully raise the window to pretty much press it into the top channel. Only very slightly though as my car has one of those not required ‘safety’ features that if it detects any unexpected resistance it panics and winds the window back down again. Grrr. But managed to get it just right and et voici:

A bit of wavy line syndrome, both from the cardboard cutting and the jigsaw but more than close enough for this job.
I then used the offcut to cut a thin strip to attach to the outside as a cover for the plastic to glass joint to keep water out. A slot was cut out for the letterbox and everything drilled and screwed together with mastic to seal things up.
But we are not quite there yet.
As by design this is quite flexible, there is nothing to stop it bowing outwards from the glass at the bottom. It shouldn’t much due to being in the top window channel but it wouldn’t be a G1YBB design if I didn’t deal with that.
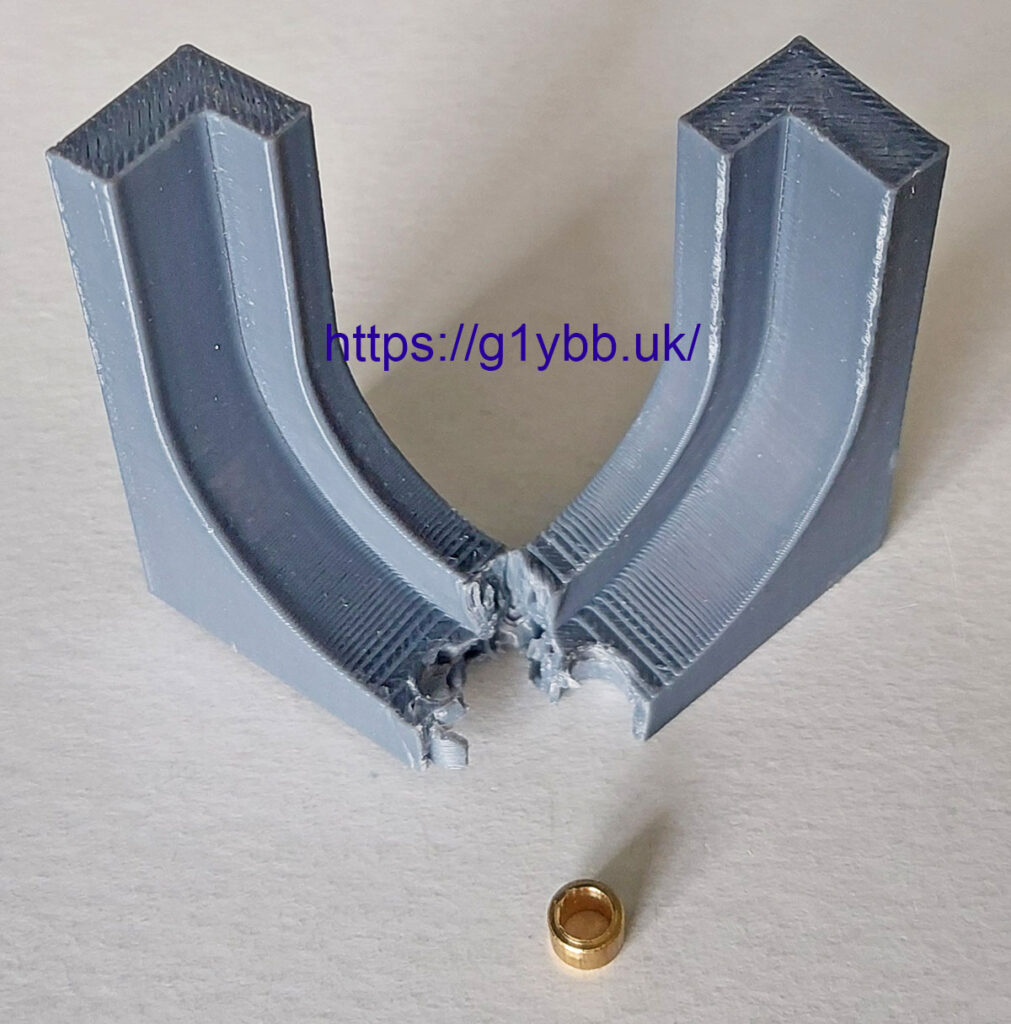
A few minutes in 3D CAD and a few more on the 3D printer and I had two clips to fit to the inside. It has a 1.5mm thick step (3mm polypropylene + 1.5mm > 4mm glass) and a tab to slide the glass past.
These were fitted then the assembly left over the weekend to give the mastic some time to set.
And here is how it looks on the maiden test fit:
If I can get a photo in the next UKAC I will but setup is now in the dark. I’ll definitely take one from the inside though and update soon!.